Edible Forest Gardening:
Edible forest gardening: Have you ever imagined a garden that not only provides stunning beauty but also offers a bountiful supply of fresh and delicious food? Well, that’s exactly what edible forest gardening is all about!
Picture this: instead of rows of neat little vegetable patches, imagine a vibrant and thriving ecosystem where trees, shrubs, herbs, and vines grow together in harmony. In an edible forest garden, nature’s design takes center stage, and the result is a sustainable and diverse paradise.
So, whether you’re a nature lover, an aspiring gardener, or simply someone who wants to learn more about sustainable living, join me as we dive into the fascinating world of edible forest gardening and discover how we can create a flourishing oasis right in our own backyards.
Step 1: Choose the right location for your garden.
Step 2: Design the layout, considering the different layers.
Step 3: Select a variety of plants that are suitable for your climate.
Step 4: Prepare the soil by removing weeds and adding compost.
Step 5: Plant your chosen trees, shrubs, and groundcovers.
Remember to regularly maintain your garden by watering, mulching, and pruning. Enjoy the abundance of natural beauty and delicious foods from your edible forest garden!
Edible Forest Gardening: A Sustainable Approach to Food Production
Edible forest gardening is a sustainable and innovative approach to food production that mimics the structure and functions of natural forests while providing a diverse range of edible plants. It combines the principles of permaculture, agroforestry, and ecological gardening to create a self-sustaining system that nurtures both plants and wildlife. This article explores the concept of edible forest gardening and its benefits, design principles, and tips for creating your own edible forest garden.
1. Understanding Edible Forest Gardening
Edible forest gardening is based on the idea that nature has already perfected a self-regulating and abundant model for growing plants. By observing and replicating the structure and dynamics of natural forests, edible forest gardeners create a harmonious and productive ecosystem. The main goal is to cultivate a wide variety of edible plants that can thrive together, benefiting from the interactions between different species.
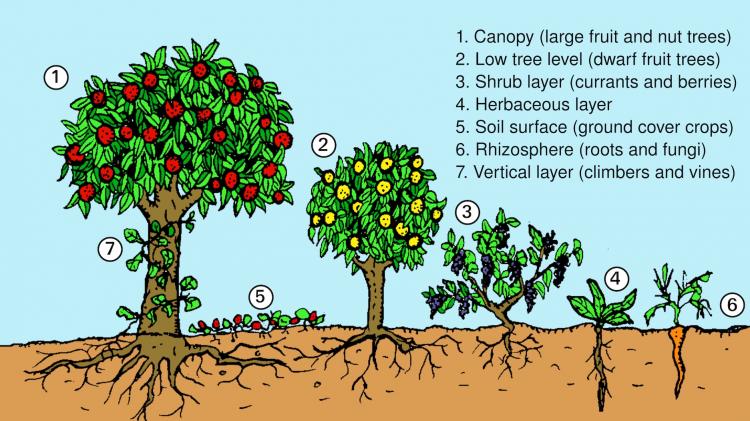
In an edible forest garden, plants are strategically chosen based on their complementarity, including their growth habits, nutrient requirements, and pollination needs. The key is to create layers within the garden, just like in a natural forest, with tall canopy trees, understory trees, shrubs, herbaceous plants, and ground covers. This approach maximizes the use of vertical space and creates a diverse and productive ecosystem.
The Benefits of Edible Forest Gardening:
Edible forest gardening offers numerous benefits, both for the environment and for the gardener. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Biodiversity: By mimicking natural ecosystems, edible forest gardens support a wide range of plant and animal species, promoting biodiversity and enhancing ecosystem health.
2. Food Security: Edible forest gardens are highly resilient and can provide a diverse and abundant supply of food throughout the year. They are less vulnerable to climate change and require less maintenance compared to traditional gardens.
3. Soil Health: The diverse plant species in an edible forest garden work together to improve soil fertility, enhance water retention, and prevent erosion. This reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and promotes sustainable soil management.
4. Carbon Sequestration: Forest gardens play a crucial role in sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, mitigating the effects of climate change.
5. Low Maintenance: Once established, edible forest gardens require minimal maintenance as they are designed to be self-regulating and self-sustaining. This makes them ideal for busy individuals or those with limited gardening experience.
2. Design Principles for Edible Forest Gardening
Designing an edible forest garden requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. Here are some important design principles to keep in mind:
1. Canopy Trees: Choose large fruit or nut trees as the backbone of your edible forest garden. These trees provide shade, support climbing plants, and act as hosts for beneficial insects.
2. Understory Trees: Plant smaller fruit and nut trees beneath the canopy trees. These trees will thrive in the partial shade and contribute to the overall productivity of the garden.
3. Shrubs and Bushes: Integrate a variety of shrubs and bushes that produce edible fruits, berries, or nuts. These plants will occupy the middle layer of the garden and provide additional food sources.
4. Herbaceous Plants: Include a range of herbaceous plants such as vegetables, herbs, and medicinal plants. These plants will fill the lower layers of the garden and provide diversity in flavor and culinary uses.
5. Ground Covers: Select low-growing plants or cover crops that can act as living mulch, suppressing weeds, retaining moisture, and enriching the soil.
6. Companion Planting: Take advantage of the interactions between different plant species by practicing companion planting. Some plants can enhance each other’s growth, deter pests, or attract beneficial insects.
Tips for Creating Your Own Edible Forest Garden:
1. Start Small: Begin with a small section of your yard to experiment with the concept of edible forest gardening. As you gain experience and confidence, you can gradually expand your garden.
2. Consider Climate and Soil: Choose plant species that are well-adapted to your climate and soil conditions. Research local native plants and traditional food crops to ensure success.
3. Plan for Succession: Incorporate a variety of plants with staggered maturity times to ensure a continuous harvest throughout the year. This will provide a more sustainable food source.
4. Embrace Diversity: Aim for a diverse mix of plant species to maximize the resilience and productivity of your garden. This includes selecting plants of different sizes, shapes, and functions.
5. Practice Organic Gardening Methods: Eliminate the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Instead, focus on building healthy soil through composting, mulching, and natural pest control methods.
6. Observe and Adapt: Observe how your garden evolves over time and make adjustments as needed. Nature is your best teacher, so pay attention to the interactions between plants and the overall health of the ecosystem.
3. The Future of Edible Forest Gardening
As the world grapples with issues of food security, environmental degradation, and climate change, the concept of edible forest gardening offers a sustainable and innovative solution. By harnessing the power of nature and working with ecosystems rather than against them, we can create vibrant and regenerative landscapes that provide abundant food for generations to come.
The potential of edible forest gardening goes beyond individual gardens. It has the power to transform entire neighborhoods, communities, and even urban areas into flourishing edible landscapes. Imagine walkable streets lined with fruit trees, public parks filled with edible herbs and greens, and rooftops transformed into lush gardens. Edible forest gardening has the potential to revolutionize the way we perceive and interact with our urban environments, making cities more resilient, sustainable, and delicious.
In conclusion, edible forest gardening offers a sustainable and regenerative approach to food production. By emulating the structure and functions of natural forests, we can create self-sustaining ecosystems that provide an abundance of food while supporting biodiversity and mitigating climate change. Whether you have a large plot of land or a tiny balcony, you can embrace the principles of edible forest gardening and contribute to a more resilient and delicious future. So grab your shovel, plant some seeds, and embark on the journey of creating your own edible forest garden. Happy gardening!
Key Takeaways: Edible Forest Gardening
- Edible forest gardening combines the concept of permaculture with the practice of growing food in a forest-like ecosystem.
- It focuses on growing a diverse range of edible plants, including trees, shrubs, and groundcover, to create a sustainable and self-sufficient food system.
- By mimicking natural forest ecosystems, edible forest gardens enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and conserve water.
- They provide a year-round supply of nutritious fruits, nuts, and vegetables, reducing dependence on store-bought produce.
- Edible forest gardening offers opportunities for community building, education, and reconnecting with nature while promoting sustainable living.
Frequently Asked Questions
Edible forest gardening is an innovative approach to gardening that mimics the structure and function of a natural forest ecosystem. It focuses on planting a variety of edible plants, including fruit trees, shrubs, and herbaceous plants, in a way that maximizes biodiversity and ecological stability. Here are some common questions and answers about edible forest gardening:
1. How does edible forest gardening work?
Edible forest gardening works by emulating the layers of a natural forest ecosystem. The garden is designed to have multiple layers of vegetation, including tall canopy trees, understory trees, shrubs, herbaceous plants, climbers, and groundcovers. Each layer serves a specific purpose and creates a balanced and self-sustaining ecosystem. For example, tall canopy trees provide shade and create a microclimate for the plants below, while groundcovers help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
2. What are the benefits of edible forest gardening?
Edible forest gardening offers a range of benefits. First and foremost, it provides a sustainable source of fresh and nutritious food. By growing a variety of edible plants, you can reduce your dependence on store-bought produce and enjoy a diverse and healthy diet. Additionally, edible forest gardens are low-maintenance and require minimal inputs such as water and fertilizer. They also enhance biodiversity and provide habitat for wildlife, promoting a more balanced and resilient ecosystem. Plus, edible forest gardens can be aesthetically pleasing, creating beautiful and naturalistic landscapes.
3. Can I implement edible forest gardening in a small space?
Yes, edible forest gardening can be adapted to fit spaces of different sizes, including small urban yards or even balconies. The key is to utilize vertical space and choose the right plants. Instead of planting tall canopy trees, you can opt for dwarf or columnar fruit trees that take up less space. Shrubs and climbers can be trained against walls or trellises, and herbaceous plants can be grown in containers. Even in limited spaces, you can create a multi-layered garden that maximizes productivity and biodiversity.
4. How do you maintain an edible forest garden?
Edible forest gardens are designed to be self-sustaining, requiring minimal maintenance once established. Regular tasks include mulching, pruning, and harvesting. Mulching helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil fertility. Pruning is necessary to maintain the desired structure and productivity of the garden. Harvesting should be done regularly to enjoy the fruits of your labor and prevent overcrowding. Overall, the goal is to create a balanced and resilient ecosystem where the plants support each other and minimize the need for external inputs.
5. Can I convert an existing garden into an edible forest garden?
Yes, it is possible to convert an existing garden into an edible forest garden. However, it may require some modifications and planning. Assess the existing plants in your garden and determine which ones can be incorporated into the edible forest garden design. Remove any plants that are not compatible or do not fit the desired structure. Consider adding new plants that contribute to the layers and functions of the ecosystem. Gradually introduce the edible plants, ensuring proper spacing and sunlight requirements. With time and careful management, your existing garden can transform into a productive and diverse edible forest garden.

A Forest Garden With 500 Edible Plants Could Lead to a Sustainable Future | Short Film Showcase
Summary
Edible forest gardening is a cool way to grow food and help the environment. It’s like having a mini forest in your backyard that you can eat from. By using different layers of plants – like tall trees, small trees, shrubs, and groundcovers – you can create a diverse ecosystem that provides food, shade, and shelter for animals. It’s a win-win for nature and our tummies!
Building an edible forest garden takes some planning and patience, but it’s worth it. You need to choose the right plants for your climate and make sure they get the right amount of sun and water. Once your garden is set up, you can enjoy a variety of delicious fruits, veggies, and herbs all year round. Plus, you’re helping to protect the planet by reducing the need for industrial agriculture and supporting biodiversity. So grab a shovel and get ready to grow your own edible forest!
